最近在写 virtual dom 方面的逻辑,用到 BFS 和 DFS。总结一波~
Virtual Dom 的示例 json 如下:
const vNode = {
node: "root",
child: [
{
node: "element1",
child: [
{
node: "element3"
},
{
node: "element4"
}
]
},
{
node: "element2"
}
]
};
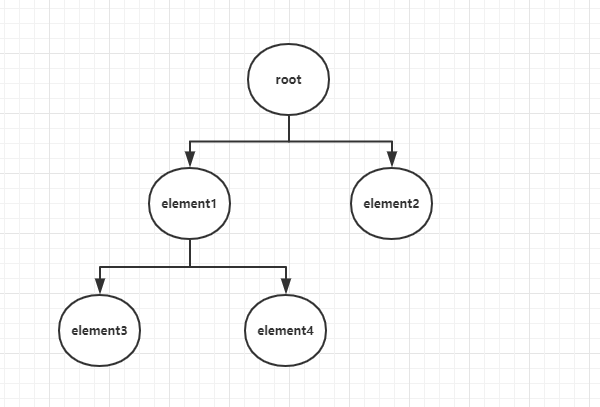
Virtual Dom 的树如下:
# 广度优先搜索 BFS
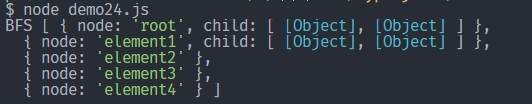
BFS :逐层访问节点,从左到右访问完成一层访问后,访问下一层,且每个节点只访问一次。
上面的树用 BFS 顺序就是:root -> element1 -> element2 -> element3 -> element4。
实现思路:
- 设置队列
queue,就将根节点添加到队列queue; - 判断当队列
queue是否为空,不为空则弹出队头节点currentNode; - 将队头节点
currentNode添加到结果队列lists; - 判断队头节点
currentNode是否有子节点,有则将子节点从左到右依次添加到队列queue; - 重复步骤2~4。
简单理解就是:
- 根节点进队列;
- 判断队头节点是否子节点,有则将子节点从左到右依次进队列,队头节点出队列。
- 重复2。
用 js 代码实现如下:(注意:判断条件为队列长度)
/**
* BFS 非递归写法
* @param {*} root 根节点
*/
const BFS = root => {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(root) != '[object Object]') {
throw(new Error('root 类型错误!'));
return;
}
let resLists = []; // 存放 BFS 节点队列
if (!Object.keys(root).length) {
return lists;
}
let queue = []; // 临时队列,每遇到一个节点就存放进队列
queue.unshift(root);
while (queue.length) {
// queue 队列不为空,遍历临时队列
let currentNode = queue.pop(); // 弹出临时队列的一个节点
const hasChild =
currentNode.hasOwnProperty("child") && currentNode.child.length; // 判断当前节点是否有子节点
if (hasChild) {
const childrenNodes = currentNode.child; // 子节点数组
for (let i = 0, len = childrenNodes.length; i < len; i++) {
const currentChildNode = childrenNodes[i]; // 当前子节点
queue.unshift(currentChildNode); // 添加到队列
}
}
resLists.push(currentNode); // 当前节点存放到 BFS 节点队列
}
return resLists;
};
结果如下:
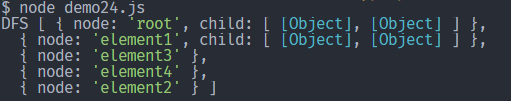
# 深度优先搜索 DFS
DFS:对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,且每个节点只访问一次。
上面的树用 BFS 顺序就是:root -> element1 -> element3 -> element4 -> element2。
实现思路1(非递归):
- 根节点进栈
stack; - 判断栈
stack是否为空,判断栈顶元素是否有有子节点,有则将栈顶元素的子节点从右到左依次进栈; - 弹出栈顶元素,存进
lists; - 重复2~3;
简单理解就是:
- 根节点进栈;
- 弹出栈顶元素,判断栈顶元素是否子节点,有则将子节点从右到左依次进栈;
- 重复2。
代码如下:(注意:判断条件为栈长度)
const DFS = root => {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(root) != "[object Object]") {
throw new Error("root 类型错误!");
}
let resLists = []; // 存放 BFS 节点队列
if (!Object.keys(root).length) {
return lists;
}
let stack = []; // 栈,每遇到一个节点就存放进栈
stack.push(root);
while (stack.length) {
let currentNode = stack.pop(); // 弹出栈顶元素
const hasChild =
currentNode.hasOwnProperty("child") && currentNode.child.length; // 判断当前节点是否有子节点
if (hasChild) {
const childrenNodes = currentNode.child; // 子节点数组
for (let i = childrenNodes.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const currentChildNode = childrenNodes[i]; // 当前子节点
stack.push(currentChildNode); // 添加到队列
}
}
resLists.push(currentNode); // 当前节点存放到 DFS 结果列表
}
return resLists;
};
实现思路2(递归):
- 当前节点入栈
stack; - 判断当前节点是否有子节点;
- 有子节点:
- 将子节点从右到左依次进行递归;(栈是先进后出 )
- 所有子节点递归结束,当前节点出栈;
- 无:
- 当前节点出栈。
代码实现如下:(注意:判断关键为节点是否有子节点)
var stack = []; // 栈
var lists = []; // 存放 DFS 节点
/**
* 全局变量实现
* @param {*} currentNode : 当前节点
*/
const DFS = currentNode => {
let hasChild =
currentNode.hasOwnProperty("child") && currentNode.child.length; // 判断当前节点是否有子节点
stack.push(currentNode); // 推入栈
if (hasChild) {
let len = currentNode.child.length;
for (let i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const currentChildNode = currentNode.child[i]; // 当前子节点
DFS(currentChildNode); // 递归
}
lists.unshift(stack.pop()); // 出栈
} else {
lists.unshift(stack.pop()); // 出栈
}
};
/**
* 非全局变量方式实现
* @param {*} currentNode : 当前节点
* @param {*} cache : 缓存栈和节点
*/
const DFS = (currentNode = {}, cache = { lists: [], stack: [] }) => {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(currentNode) != "[object Object]") {
throw new Error("root 类型错误!");
}
let hasChild =
currentNode.hasOwnProperty("child") && currentNode.child.length; // 判断当前节点是否有子节点
let { lists, stack } = cache;
stack.push(currentNode); // 推入栈
if (hasChild) {
let len = currentNode.child.length;
for (let i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 注意这里要从右向左循环,因为 stack 是先进后出
const currentChildNode = currentNode.child[i]; // 当前子节点
const {
lists: newLists,
stack: newStack
} = DFS(currentChildNode, {
lists,
stack
}); // 递归
lists = newLists; // 更新 lists
stack = newStack; // 更新栈
}
lists.unshift(stack.pop()); // 出栈
} else {
lists.unshift(stack.pop()); // 出栈
}
// 函数返回结果,如果栈中还有节点,证明还没回溯完成,则返回缓存;否则函数执行结束
const res = stack.length
? {
lists: lists,
stack: stack
}
: lists;
return res;
};
结果如下: