# 问题
之所以会有这个问题,是因为在做静态网站的时候,SEO 人员发现文本前后空格的问题,并提出文本前后不要有前后空格的需求。
用 SPA 做测试,Vue 在解析 template 中标签文本会有以下两种情况:
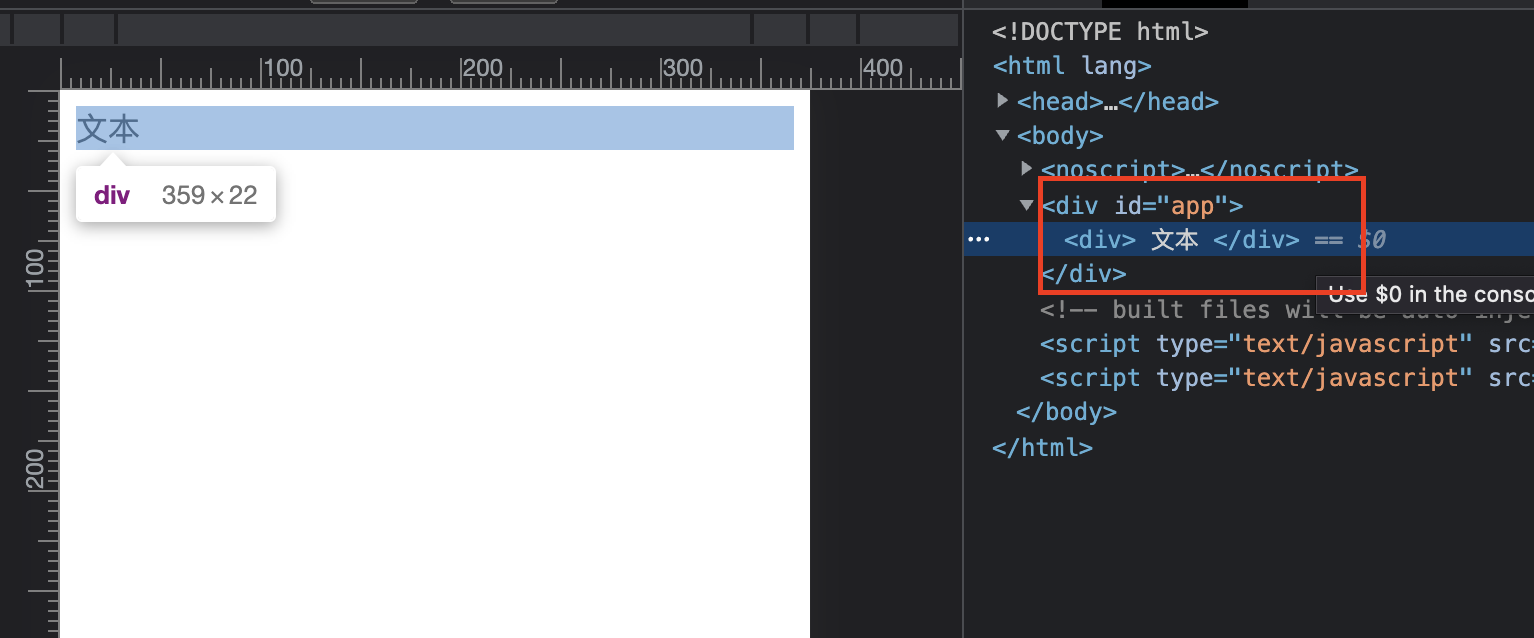
- 标签内换行
<div>
文本
</div>
在浏览器渲染为:
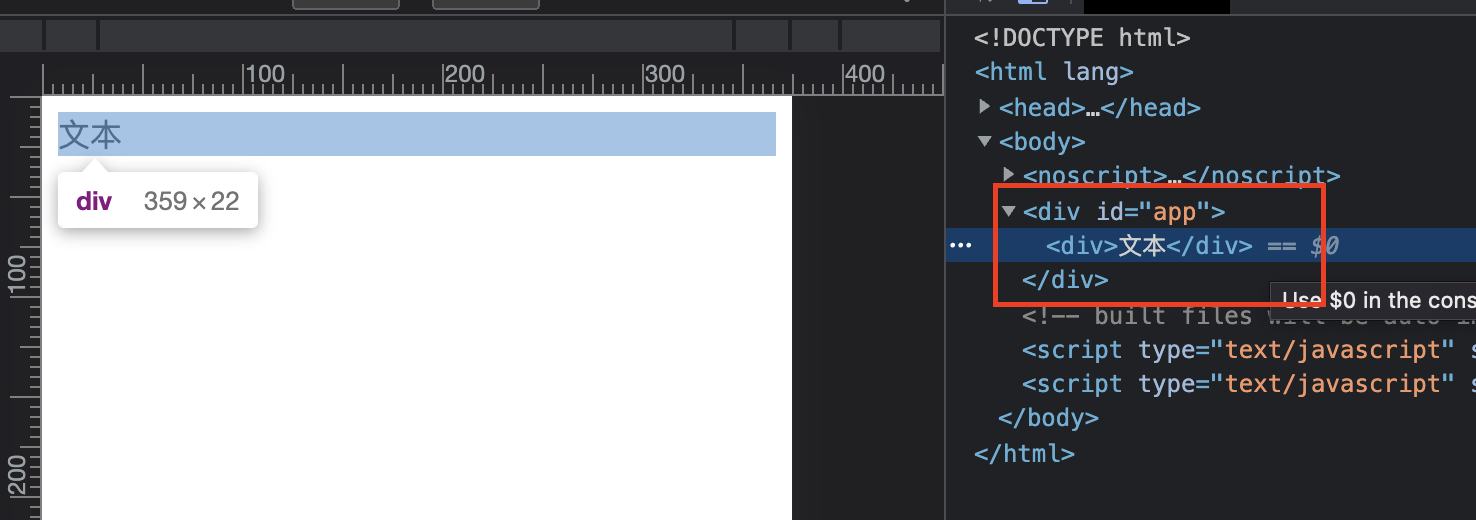
- 标签内不换行
<div>文本</div>
在浏览器渲染为:
之前也做过 SSR 的测试。发现该问题不仅仅在 SSR,SPA 也存在该问题。
对问题定位:
在解析 vue 单文件 template 模版的时候对换行做了特殊处理,也就是 vue-loader (opens new window) 这个 loader。
如果不是通过 .vue 文件渲染页面,而是通过 template 模版字符串渲染,则不会 vue-loader 转化逻辑,而是通过 vue 内部的 compile 和 compileToFunctions 进行转化。主要代码如下:
function createCompilerCreator(baseCompile) {
// ...
}
var createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile (
template,
options
) {
// ...
})
var ref$1 = createCompiler(baseOptions);
var compile = ref$1.compile;
var compileToFunctions = ref$1.compileToFunctions;
不管是通过 vue-loader 还是内部编译逻辑,其核心都是使用 vue-template-compiler (opens new window) 这个插件。
# vue-template-compiler (opens new window)
查看文档,发现有 vue-template-compiler 有一个 whitespace 配置项:
- preserve:默认项。
- 元素标签之间的纯空白文本节点被压缩为一个空格。
- 所有其他空格按原样保留。
- condense
- 如果元素标签之间的纯空白文本节点包含新行,则会被删除。否则,它会被压缩为一个空格。
- 非纯空格文本节点内的连续空格被压缩为一个空格。
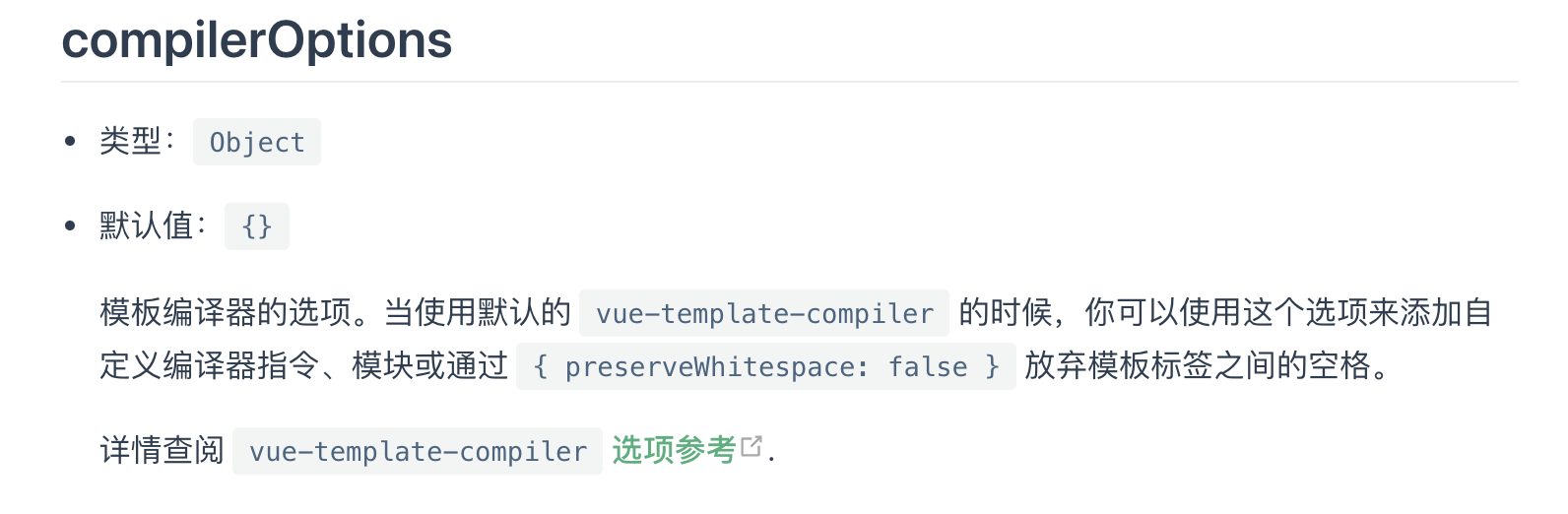
在 vue 项目中执行 vue inspect > output.js 查看 webpack 配置,找到 vue-loader 的配置,有如下配置:
{
options: {
compilerOptions: {
whitespace: 'condense'
}
}
}
发现 vue-loader 的配置选项中的 compilerOptions 的 whitespace 设置为 'condense'。查看 vue-loader 文档链接 (opens new window),有 compilerOptions (opens new window) 配置说明,该配置项最终的配置就是 vue-template-compler 的 whitespace 配置。
# 查看 vue-template-compiler 源码
# compile 函数
文件vue-template-compiler/build.js,使用的 compile 方法定义的主要代码为:
function createCompilerCreator (baseCompile) {
return function createCompiler (baseOptions) {
function compile (
template,
options
) {
// ...
var compiled = baseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions);
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
detectErrors(compiled.ast, warn);
}
compiled.errors = errors;
compiled.tips = tips;
return compiled
}
return {
compile: compile
}
}
}
var createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile (
template,
options
) {
var ast = parse(template.trim(), options);
if (options.optimize !== false) {
optimize(ast, options);
}
var code = generate(ast, options);
return {
ast: ast,
render: code.render,
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
}
});
var ref = createCompiler(baseOptions);
var compile = ref.compile;
exports.compile = compile;
compile 函数的定义:通过 createCompilerCreator 高阶函数返回的函数获取 createCompiler,再通过函数 createCompiler 返回的对象获取 compile 函数。
compile 函数的执行:实际上就是执行createCompilerCreator -> createCompiler -> compile -> baseCompile,compile 方法内部主要执行传入的 baseCompile 函数。
梳理下来,compile 函数主要执行逻辑的就是传入 createCompilerCreator 函数的 baseCompile 实参.
而 baseCompile 函数内部执行解析逻辑的是 parse 函数,流程跟常规的编译器基本一样,分为三个:
- parse 解析
- optimize 优化
- generate 生成
# parse 函数
主要作用是将代码解析成 AST。
parse 函数的参数有两个:
- template 模板字符串
- option 配置项
函数内部先处理 options 并定义了一系列工具函数,然后调用 parseHTML 解析 template,最后返回根节点 root。
主要源码如下:
function parse (
template,
options
) {
// 处理 options
// ...
// 定义工具函数
// ...
// 调用 parseHTML 函数
parseHTML(template, {
// options
start: function start (tag, attrs, unary, start$1, end) {
// ...
},
end: function end (tag, start, end$1) {
// ...
},
chars: function chars (text, start, end) {
// ...
},
comment: function comment (text, start, end) {
// ...
}
})
return root
}
传递给 parseHTML 的参数除了 template 模版和 options 选项外,还有四个函数:
- start: 处理开始标签。主要逻辑为:为当前的标签创建 AST 对象,将当前 AST 对象入 stack 栈,最后将当前 AST 赋值给 currentParent 当作下一个标签的父节点。
- end: 处理结束标签。判断当前标签是否为栈顶元素,并出栈。
- chars: 处理文本字符串。上面提及的 whitespace 配置项就是在这里面处理的。
- comment: 处理注释。
# parseHTML 函数
这里根据下面的 html 字符串整理流程:
<div>
<span>
文本
</span>
</div>
开始循环遍历 html 字符串,直到 html 全部遍历完。
while (html) {
// ...
}
第一次循环。
匹配标签开始标志<,根据当前匹配到的索引 textEnd 判断标签当前文本类型:
- textEnd 为 0:当前 html 以标签开始。
- textEnd 大于 0:当前 html 以文本开始。
- textEnd 小于 0:html 遍历结束。
while (html) {
// ...
var textEnd = html.indexOf('<');
if (textEnd === 0) {
// ...
}
if (textEnd >= 0) {
// ...
}
if (textEnd < 0) {
// ...
}
// ...
}
回到例子,html 匹配标签开始标志<,textEnd 为 0,说明当前 html 是以标签开始。
接着进入 parseStartTag 处理函数,该函数主要是获取标签名,还有标签在当前 html 中的开始索引 start 和结束索引 end。{ tagName: 'div', attrs: [], start: 0, unarySlash: '', end: 5 }
然后通过 advance 函数将 html 剔除开始标签字符串。
function advance (n) {
index += n;
html = html.substring(n);
}
最后执行通过参数传入 parseHTML 函数的 options.start,该函数会根据当前标签创建 AST 元素对象,并将当前 AST 对象的 parent 设置为父节点 currentParent,最后将 AST 对象入栈 stack,并将当前 AST 赋值给 currentParent 当作下一个标签的父节点。
由于第一次循环,root 为空,会将当前 AST 元素对象赋值给 root 变量。
parstHTML(template, {
start: function start(tag, attrs, unary, start$1, end) {
// ...
var element = createASTElement(tag, attrs, currentParent);
// ...
if (!root) {
root = element;
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
checkRootConstraints(root);
}
}
// ...
if (!unary) {
currentParent = element;
stack.push(element);
} else {
closeElement(element);
}
}
})
第一次循环结束,会得到:
下次循环的 html:
<span>
文本
</span>
</div>
stack:
[{
"type": 1,
"tag": "div",
"attrsList": [],
"attrsMap": {},
"rawAttrsMap": {},
"children": []
}]
第二次循环。
剩下的 html 匹配标签开始标志<,textEnd 大于 0,说明当前 html 到下一个标签之前存在文本。
接着通过执行通过text=html.substring(0, textEnd)获取文本内容。
然后通过 advance 函数将 html 剔除开始标签字符串。
最后执行通过参数传入 parseHTML 函数的 options.chars,该函数会根据不同配置项对文本格式做不同的处理。
如果 text 文本做trim()处理之后为空,并且父节点 currentParent 的 children 为空,说明当前 text 文本为父节点和第一个字节点之前的标签内容,则直接将 text 设置为空,直接返回。
parstHTML(template, {
chars: function chars(text, start, end) {
// ...
if (inPre || text.trim()) {
text = isTextTag(currentParent) ? text : decodeHTMLCached(text);
} else if (!children.length) {
// remove the whitespace-only node right after an opening tag
text = '';
} else if (whitespaceOption) {
if (whitespaceOption === 'condense') {
// in condense mode, remove the whitespace node if it contains
// line break, otherwise condense to a single space
text = lineBreakRE.test(text) ? '' : ' ';
} else {
text = ' ';
}
} else {
text = preserveWhitespace ? ' ' : '';
}
}
})
如果 text 文本做trim()处理之后不为空,则将处理好的 text 文本内容设置为父节点 currentParent 的子节点。
preserve:默认项。
- 元素标签之间的纯空白文本节点被压缩为一个空格。
- 所有其他空格按原样保留。
condense
- 如果元素标签之间的纯空白文本节点包含新行,则会被删除。否则,它会被压缩为一个空格。
- 非纯空格文本节点内的连续空格被压缩为一个空格。
if (!inPre && whitespaceOption === 'condense') { // condense consecutive whitespaces into single space text = text.replace(whitespaceRE, ' '); }
回到例子,由于当前获取的文本 text 做trim()处理之后为空,并且父节点 currentParent 的 children 为空,会直接将 text 设置为空,并结束当前循环。
第二次循环结束,会得到:
下次循环的 html:
<span>
文本
</span>
</div>
stack 内容不变。
第三次循环。
剩下的 html 匹配标签开始标志<,textEnd 为 0,说明当前 html 是以标签开始。
接着进入 parseStartTag 处理函数,该函数主要是获取标签名,还有标签在当前 html 中的开始索引 start 和结束索引 end。{ tagName: 'span', attrs: [], start: 8, unarySlash: '', end: 14 }
然后通过 advance 函数将 html 剔除开始标签字符串。
最后执行通过参数传入 parseHTML 函数的 options.start,该函数会根据当前标签创建 AST 元素对象,当后将 AST 对象入栈 stack,并将当前 AST 赋值给 currentParent 当作下一个标签的父节点。
第三次循环结束,会得到:
下次循环的 html:
文本
</span>
</div>
stack:
[
{
"type": 1,
"tag": "div",
"attrsList": [],
"attrsMap": {},
"rawAttrsMap": {},
"children": []
},
{
"type": 1,
"tag": "span",
"attrsList": [],
"attrsMap": {},
"rawAttrsMap": {},
"parent": {
"type": 1,
"tag": "div",
"attrsList": [],
"attrsMap": {},
"rawAttrsMap": {},
"children": []
},
"children": []
}
]
第四次循环。
剩下的 html 匹配标签开始标志<,textEnd 大于 0,说明当前 html 到下一个标签之前存在文本。
接着通过执行通过text=html.substring(0, textEnd)获取文本内容。
然后通过 advance 函数将 html 剔除开始标签字符串。
由于 text 文本做trim()处理之后不为空,则将处理好的 text 文本内容设置为父节点 currentParent 的子节点。
第四次循环结束,会得到:
下次循环的 html:
</span>
</div>
stack:
[
{
"type": 1,
"tag": "div",
"attrsList": [],
"attrsMap": {},
"rawAttrsMap": {},
"children": []
},
{
"type": 1,
"tag": "span",
"attrsList": [],
"attrsMap": {},
"rawAttrsMap": {},
"parent": {
"type": 1,
"tag": "div",
"attrsList": [],
"attrsMap": {},
"rawAttrsMap": {},
"children": []
},
"children": [
{
"type": 3,
"text": " 文本 "
}
]
}
]
第五次循环。
剩下 html 匹配标签开始标志<,textEnd 为 0,说明当前 html 是以标签开始。
接着在判断是结束标签,则通过 advance 函数将 html 剔除开始标签字符串。
然后进入 parseEndTag 函数,调用通过参数传入 parseHTML 函数的 options.end,将当前标签弹出栈 stack。
第五次循环结束,会得到:
下次循环的 html:
</div>
stack:
[
{
"type": 1,
"tag": "div",
"attrsList": [],
"attrsMap": {},
"rawAttrsMap": {},
"children": []
}
]
第六次循环。
跟第五次一样。最后 html 遍历结束,stack 也为空了。
parseHTML 执行结束,返回 root 根对象。