# 源码
在 vue 源码中,双向数据绑定的实现在 initState 中。
function initState (vm) {
vm._watchers = [];
var opts = vm.$options;
if (opts.props) { initProps(vm, opts.props); }
if (opts.methods) { initMethods(vm, opts.methods); }
// 处理 data 数据
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm);
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */);
}
if (opts.computed) { initComputed(vm, opts.computed); }
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch);
}
}
对于 data 的处理,如果 vue 实例中有定义 data 属性,则调用 initData 处理,没有的话则将 _data 设置为空对象,然后直接调用 observe 函数处理。由于在 initData 函数也会调用 observe 函数,故直接看 initData 函数。
# initData 函数
function initData (vm) {
var data = vm.$options.data;
// 如果 data 是个函数,则调用 getData 函数获取 data 数据;否则的话直接使用 data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {};
if (!isPlainObject(data)) {
data = {};
warn(
'data functions should return an object:\n' +
'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',
vm
);
}
// 代理 data 数据,当通过 this.xxx 获取 data 数据时,实际上是访问了 this._data.xxx
var keys = Object.keys(data);
var props = vm.$options.props;
var methods = vm.$options.methods;
var i = keys.length;
while (i--) {
var key = keys[i];
{
if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {
warn(
("Method \"" + key + "\" has already been defined as a data property."),
vm
);
}
}
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
warn(
"The data property \"" + key + "\" is already declared as a prop. " +
"Use prop default value instead.",
vm
);
} else if (!isReserved(key)) {
proxy(vm, "_data", key);
}
}
// observe data
// 实现数据劫持
observe(data, true /* asRootData */);
}
函数主要执行逻辑:
判断 data 类型,如果 data 是个函数,则调用 getData 函数获取 data 数据;否则的话直接使用 data。getData 函数源码如下:
function getData (data, vm) { // 添加当前目标,初始化的时候,target 为空 pushTarget(); try { return data.call(vm, vm) // 绑定到当前实例 } catch (e) { handleError(e, vm, "data()"); return {} } finally { popTarget(); // 推出当前 target } } Dep.target = null; var targetStack = []; function pushTarget (target) { targetStack.push(target); Dep.target = target; } function popTarget () { targetStack.pop(); Dep.target = targetStack[targetStack.length - 1]; }遍历对象,调用 proxy 方法对 data 对象的每一项进行代理处理。当通过 this.xxx 获取 data 数据时,实际上是访问了 this._data.xxx。proxy 方法源码如下:
function proxy (target, sourceKey, key) { // data 的 get 处理 sharedPropertyDefinition.get = function proxyGetter () { return this[sourceKey][key] }; // data 的 set 处理 sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function proxySetter (val) { this[sourceKey][key] = val; }; Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition); }调用 observe 函数实现数据劫持。
# observe 函数
function observe (value, asRootData) {
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
var ob;
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__;
} else if (
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
ob = new Observer(value);
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++;
}
return ob
}
函数执行逻辑:
- 判断数据是不是对象,不是对象直接返回。
- 判断当前数据是否已经处理过:
- 处理过,即包含
__ob__属性,直接获取原先的__ob__,即:Observer 实例。 - 没处理过,实例化 Observer 对象。
- 处理过,即包含
- 返回 Observer 实例。
# Observer 对象
var Observer = function Observer (value) {
this.value = value;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
def(value, '__ob__', this); // 在当前数据对象上设置 __ob__ 属性,值为当前 Observer 实例。
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
// 数组方法处理
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods);
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys);
}
// 数组类型处理,observeArray 函数通过遍历对数组每一项做 observe 处理
this.observeArray(value);
} else {
// 对象类型,调用 walk 函数处理
this.walk(value);
}
};
函数执行逻辑:
存储当前值 value。
实例化 Dep 对象。Dep 对象主要用于设置 uid 和 存储订阅者列表。Dep 对象的源码如下:
var uid = 0; /** * A dep is an observable that can have multiple * directives subscribing to it. */ var Dep = function Dep () { this.id = uid++; this.subs = []; // 订阅者列表 };如果处理数据为数组类型。
- 先将数组原型上的所有方法直接挂到当前实例上。如果有
__proto__属性的话,则在其上挂载 Array.prototype,如果没有__proto__属性的话,则遍历 Array.prototype,在数组上直接定义所有的原型方法。 - 然后调用 observeArray 函数通过遍历对数组每一项做 observe 处理。
var arrayProto = Array.prototype; var arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto); var arrayKeys = Object.getOwnPropertyNames(arrayMethods); function protoAugment (target, src) { /* eslint-disable no-proto */ target.__proto__ = src; /* eslint-enable no-proto */ } function copyAugment (target, src, keys) { for (var i = 0, l = keys.length; i < l; i++) { var key = keys[i]; def(target, key, src[key]); } } function def (obj, key, val, enumerable) { Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { value: val, enumerable: !!enumerable, writable: true, configurable: true }); } // observeArray 源码,对数组每一项做 observe 处理 Observer.prototype.observeArray = function observeArray (items) { for (var i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) { observe(items[i]); } };- 先将数组原型上的所有方法直接挂到当前实例上。如果有
如果处理数据为对象类型,则调用 walk 函数处理。函数内部遍历对象,然后对每项调用 defineReactive$$1 函数做处理。
Observer.prototype.walk = function walk (obj) { var keys = Object.keys(obj); for (var i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) { defineReactive$$1(obj, keys[i]); } };
# defineReactive$$1 函数
function defineReactive$$1 (
obj,
key,
val,
customSetter,
shallow
) {
var dep = new Dep(); // 新建 Dep 实例,内部逻辑存储订阅者列表
// 获取当前数据对应的属性描述符
var property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key);
// 判断当前数据对象是否为不可配置,是的话直接返回。在实际项目应用中,可通过设置对象的 configurable 为 false 从而不进行数据劫持和发布订阅处理。
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// 获取访问器函数(getter)和设置器函数(setter)
var getter = property && property.get;
var setter = property && property.set;
// 如果当前数据没有 val 值,且没有访问器函数(getter)但有设置器函数(setter),则手动获取对应值
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key];
}
var childOb = !shallow && observe(val); // 获取子 observer 实例(是对象类型才会返回子 observer)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
var value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
if (Dep.target) { // 如果有当前订阅目标
dep.depend(); // 则向 dep 实例的 subs 订阅者列表中添加上当前订阅者
if (childOb) { // 如果有子对象的 observer 实例
childOb.dep.depend(); // 则向子对象的 observer 实例的 dep 的 subs 订阅者列表中添加上当前订阅者
if (Array.isArray(value)) { // 如果是数组类型
dependArray(value); // 则遍历数组,则数组每一项的订阅者列表中添加上当前订阅者
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
var value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
// 如果有自定义的 Setter 函数,则先调用自定义 Setter 函数
if (customSetter) {
customSetter();
}
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) { return }
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal);
} else {
val = newVal;
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal);
// 通知订阅者
dep.notify();
}
});
}
函数执行逻辑:
实例化 Dep 对象,新建 dep 实例,实例内部逻辑存储订阅者列表。
获取当前数据对应的属性描述符。
判断当前数据对象是否为不可配置,是的话直接返回。在实际项目应用中,可通过设置对象的 configurable 为 false 从而不进行数据劫持和发布订阅处理。
获取访问器函数(getter)和设置器函数(setter) 。
如果当前数据没有 val 值,且没有访问器函数(getter)但有设置器函数(setter),则手动获取对应值。
获取子 observer 实例(是对象类型才会返回子 observer)。
在 getter 函数中:
如果没有订阅者,则直接返回值。
如果有订阅者,则向当前的 dep 实例的订阅者列表 subs 添加上当前订阅者;并且如果有子 Observer 实例的话,则向子对象的 observer 实例的 dep 的 subs 订阅者列表中添加上当前订阅者;如果当前数据劫持的值为数组类型,则调用 dependArray 遍历数组,向数组每一项的 dep 实例的订阅者列表 subs 添加上当前订阅者。
function dependArray (value) { for (var e = (void 0), i = 0, l = value.length; i < l; i++) { e = value[i]; e && e.__ob__ && e.__ob__.dep.depend(); if (Array.isArray(e)) { dependArray(e); } } }
在 setter 函数中:
- 先获取旧值,如果新值跟旧值一样,则返回不做处理。
- 如果有自定义的 Setter 函数,则先调用自定义 Setter 函数。
- 如果当前属性设置器函数(setter)为不可设置,则返回不做处理。
- 设置新值,调用 dep.notify() 通过遍历 subs 列表(订阅者 watcher 列表) 通知订阅者,然后调用 watcher 的 update 函数。
Dep.prototype.notify = function notify () { // stabilize the subscriber list first var subs = this.subs.slice(); if (!config.async) { // subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async // we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct // order subs.sort(function (a, b) { return a.id - b.id; }); } // 遍历订阅者列表,调用每个 Watcher 的 update 方法 for (var i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) { subs[i].update(); } };
至此,vue 中的 data 初始化逻辑完成,data 对象的每一项的 getter 和 setter 也完成初始化。
# 依赖收集
依赖收集,是在 vue 实例挂载到实际 Dom 上进行渲染时($mount -> mountComponent)触发。
在 mountComponent 函数中会实例化一个渲染 Watcher。
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before: function before () {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate');
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */);
渲染 Watcher 实例化的时候会触发 this.get 函数,该函数内部会调用 pushTarget(this) 操作,将当前 watcher 实例(订阅者)设置到 Dep.target 上。最后通过调用 this.getter 函数即外部传入的 updateComponent 函数进行 vnode 的生成和真实 DOM 的渲染。在生成 vnode 的时候会触发 data 数据的 getter 操作。
var Watcher = function Watcher (
vm,
expOrFn,
cb,
options,
isRenderWatcher
) {
this.vm = vm;
if (isRenderWatcher) {
vm._watcher = this;
}
vm._watchers.push(this);
// 参数处理
if (options) {
this.deep = !!options.deep;
this.user = !!options.user;
this.lazy = !!options.lazy;
this.sync = !!options.sync;
this.before = options.before;
} else {
this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false;
}
this.cb = cb;
this.id = ++uid$2; // uid for batching
this.active = true;
this.dirty = this.lazy; // for lazy watchers
this.deps = [];
this.newDeps = [];
this.depIds = new _Set();
this.newDepIds = new _Set();
this.expression = expOrFn.toString();
// parse expression for getter
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn; // 设置 getter,这里为外部传入的 updateComponent 函数
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn);
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = noop;
warn(
"Failed watching path: \"" + expOrFn + "\" " +
'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' +
'For full control, use a function instead.',
vm
);
}
}
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get(); // 触发 getter 获取当前值
};
Watcher.prototype.get = function get () {
pushTarget(this); // 当前 Watcher 入栈,并将当前 watcher 实例(订阅者)设置到 Dep.target 上
var value;
var vm = this.vm;
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm); // 触发 getter 函数,这里为外部传入的 updateComponent 函数
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, ("getter for watcher \"" + (this.expression) + "\""));
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value);
}
popTarget(); // 当前 Watcher 出栈,并将 Dep.target 设置为栈顶元素
this.cleanupDeps();
}
return value
};
# Watcher 的 update 函数
触发 watcher 实例的 update 函数的执行是在:当 data 中的数据更新时,会触发 data 的 setter 函数,进而 setter 函数调用 dep 实例的 notify 函数对订阅者列表进行遍历,最后调用每个订阅者 Watcher 实例的 update 函数。
update 函数源码如下:
Watcher.prototype.update = function update () {
if (this.lazy) {
// 延迟通知订阅者标志,主要是 computed 相关数据用
this.dirty = true;
} else if (this.sync) {
// 同步更新。直接调用 watcher 上的 run 函数,run 函数内部调用 watcher 上的 get 函数,如果是渲染 Watcher 的话,则会调用回调函数 updateComponet 更新 VNode 最后更新 Dom
this.run();
} else {
// 异步更新(vue 采用的是异步更新)
queueWatcher(this);
}
};
update 函数执行逻辑:
- 如果需要延迟通知订阅者,则设置 lazy 为 true,主要是 computed 相关数据的 watcher。
- 如果是同步更新。直接调用 watcher 上的 run 函数,run 函数内部调用 watcher 上的 get 函数,如果是渲染 Watcher 的话,则会调用回调函数 updateComponet 更新 VNode 最后更新 Dom。
- 最后是异步更新,vue 采用的也是异步更新机制。
queueWatcher 函数源码如下:
function queueWatcher (watcher) {
var id = watcher.id; // 获取 watcher ID
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true;
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher);
} else {
// if already flushing, splice the watcher based on its id
// if already past its id, it will be run next immediately.
var i = queue.length - 1;
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--;
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher);
}
// queue the flush
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true;
if (!config.async) {
flushSchedulerQueue();
return
}
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue);
}
}
}
queueWatcher 函数执行逻辑为:
- 判断当前 watcher id 是否为新的 watcher,如果是添加过的 watcher 则不做处理,只对新 watcher 做处理。
- 对当前的新 watcher 进行标记,表示该 watcher 已经添加过。
- 根据 watcher 队列 queue 是否开始冲洗刷新做不同处理:
- 对当前 watcher 及 watcher 队列 queue 处理。如果 watcher 队列 queue 还没开始冲洗刷新的话,则将当前 watcher 实例添加到 watcher 队列;如果 watcher 队列 queue 已开始冲洗刷新,则根据其 id 大小,从 queue 队列从后往前找第一个比待插入 id 大的 watcher,插到其后面,表示代插入的 watcher 将下一个执行。
- 如果还没开始冲洗队列,则调用 nextTick 函数(这也是为什么 watcher 的数据更新会在下一次 DOM 循环更新宏任务结束之后执行的原因)并添加回调函数 flushSchedulerQueue。【异步更新队列官方文档 (opens new window)】
flushSchedulerQueue 函数源码如下:
function flushSchedulerQueue () {
currentFlushTimestamp = getNow();
flushing = true;
var watcher, id;
// Sort queue before flush.
// This ensures that:
// 1. Components are updated from parent to child. (because parent is always
// created before the child)
// 2. A component's user watchers are run before its render watcher (because
// user watchers are created before the render watcher)
// 3. If a component is destroyed during a parent component's watcher run,
// its watchers can be skipped.
queue.sort(function (a, b) { return a.id - b.id; });
// do not cache length because more watchers might be pushed
// as we run existing watchers
for (index = 0; index < queue.length; index++) {
watcher = queue[index];
if (watcher.before) {
watcher.before();
}
id = watcher.id;
has[id] = null;
watcher.run();
// in dev build, check and stop circular updates.
if (has[id] != null) {
circular[id] = (circular[id] || 0) + 1;
if (circular[id] > MAX_UPDATE_COUNT) {
warn(
'You may have an infinite update loop ' + (
watcher.user
? ("in watcher with expression \"" + (watcher.expression) + "\"")
: "in a component render function."
),
watcher.vm
);
break
}
}
}
// keep copies of post queues before resetting state
var activatedQueue = activatedChildren.slice();
var updatedQueue = queue.slice();
resetSchedulerState();
// call component updated and activated hooks
callActivatedHooks(activatedQueue);
callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue);
// devtool hook
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (devtools && config.devtools) {
devtools.emit('flush');
}
}
flushSchedulerQueue 函数执行逻辑为:
- 刷新前对队列按照 watcher 的 id 大小进行排序处理。这样可以确保:
- 组件从父级更新到子级。(因为父母总是在孩子之前创建)
- 组件的用户观察者在其渲染观察者之前运行(因为用户观察者在渲染观察者之前创建)。
- 如果一个组件在父组件的 watcher 运行期间被销毁,可以跳过它的观察者。
- 遍历 watcher 队列 queue。
- 调用 watcher before 钩子。渲染 watcher 的 before 钩子会调用 vue beforeUpdate 钩子。
- 调用 watcher 的 run 函数,run 函数内部调用 watcher 上的 get 函数,如果是渲染 Watcher 的话,则会调用回调函数 updateComponet 更新 VNode 最后更新 Dom。
- 对循环更新的情况进行判断断言。
- 遍历完成,在重置状态之前保留发布队列的副本,接着重置发布队列,最后调用 vue 的激活和更新钩子。
Vue 的双向数据绑定是使用发布订阅者模式、数据劫持和Object.defineProperty()(Vue 3.0 改用 Proxy)实现。核心原理如下图所示:
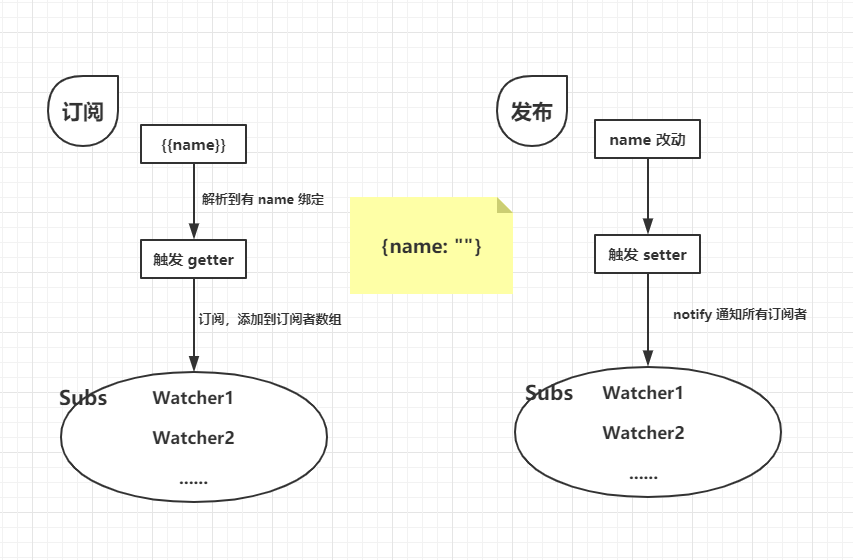
- 解析到页面中数据绑定,通过触发 getter 新增一个订阅者/观察者 Watcher 到订阅者列表 subs。
- 数据改动,通过触发 setter 通知所有的订阅者。
# 模拟实现
# 数据劫持
数据劫持是使用 Object.defineProperty()进行实现的。通过遍历数据对象 data 的所有属性,设置每个属性的 getter 和 setter 。
- 添加 observe 函数。作用是通过该函数获取当前对象的所有属性,并调用 defineReative 函数设置 getter 和 setter。
function observe(obj) {
// 过滤不是对象的值
if(!obj || Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) !== '[object Object]') {
return;
}
// 遍历对象的属性
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {
defineReative(obj, key, obj[key]); // 调用 defineReative 函数设置 getter 和 setter
})
}
- defineReative 函数。设置 getter 和 setter。
function defineReative(obj, key, val) {
observe(val); // 递归
let dp = new Dep(); // 实例化一个依赖收集对象,用于添加订阅者到订阅者列表和通知订阅者更新
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
get: function() {
if (Dep.target) { // 添加订阅者时候会将全局 Dep.target 指向 Watcher 自己,会触发 getter
dp.addSub(Dep.target);
}
return val;
},
set: function(newVal) {
val = newVal;
dp.notify(); // 通知所有的订阅者
}
})
}
# 依赖收集
- 添加 Dep 类。用于添加订阅者和通知所有订阅者更新。
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.subs = [];
}
addSub(sub) {
this.subs.push(sub);
}
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update(); // sub 指向 Watcher 实例
})
}
}
- 设置全局
Dep.target = null。用于判断是否有订阅者 Watcher 触发 getter ,有的话添加到订阅者列表。
# 订阅者
- 添加 Watcher 类。用于添加订阅者实例,通过改变全局 Dep.target ,触发 getter 并添加到订阅者列表。
class Watcher{
constructor(obj, key, cb) {
Dep.target = this; // 改变全局 Dep.target,指向自身
this.obj = obj;
this.key = key;
this.value = obj[key]; // 触发 getter 操作,并添加到订阅者列表
Dep.target = null; // 重新将 Dep.target 置为 null
}
update() {
const value = this.obj[this.key]; // 获取最新值
this.cb(value); // 通过回调更新 DOM 节点内容
}
}
# 模拟操作
- html 页面添加标签并进行数据绑定。
<div class="container">{{name}}</div>
- 添加更新 DOM 节点内容回调函数。
function update(value) {
document.querySelector(".container").innerText = value;
}
- 初始化 data 对象。
let data = {
name: "zero"
}
- 触发数据劫持。
observe(data);
- 添加订阅者。
new Watcher(data, "name", update);
- 更改 name。
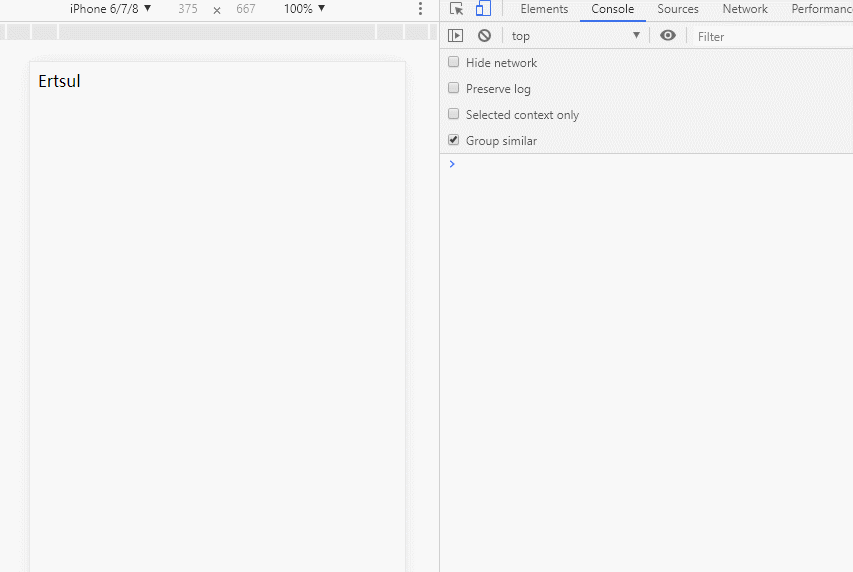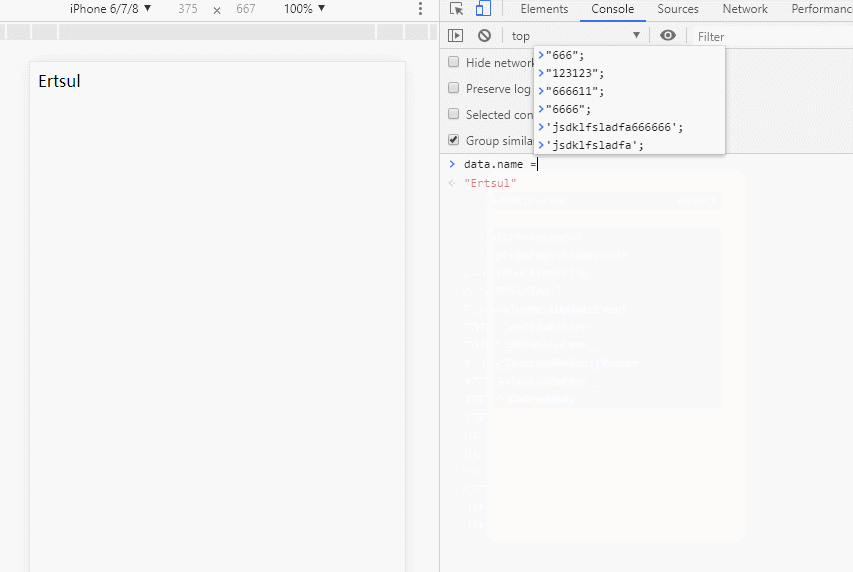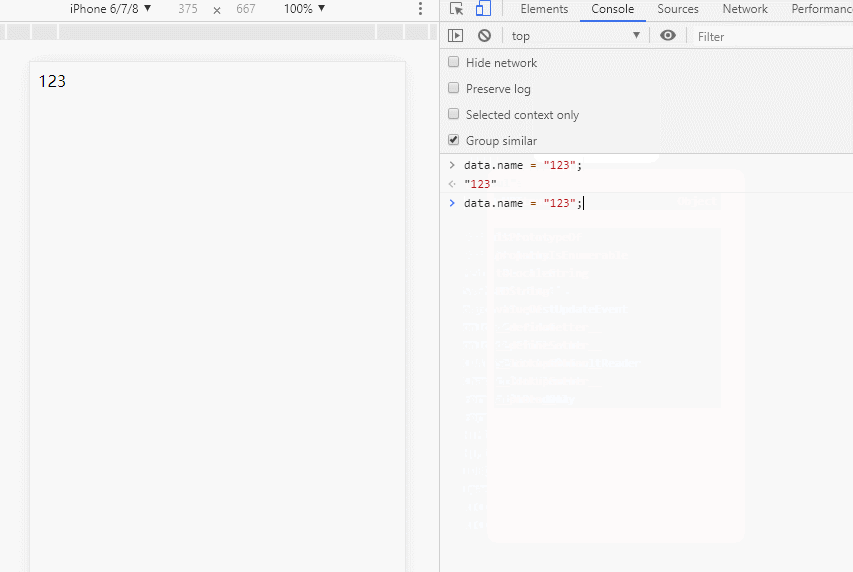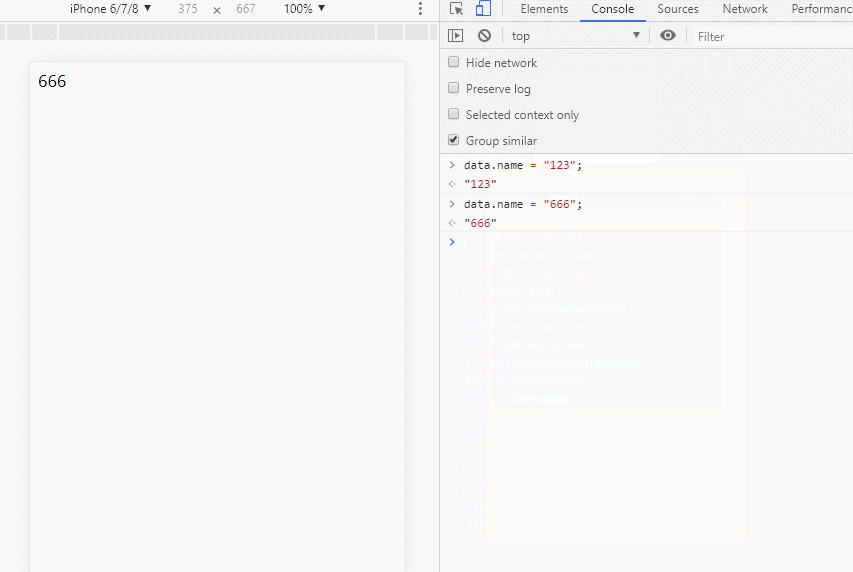
data.name = 'Ertsul';
打开浏览器,会看到 name 已经被改成 Ertsul。